Data Visualization [02]: Pandas and Seaborn Basics
Published:
matplotlib is a fairly low-level tool. pandas itself has built-in methods that simplify creating visualizations from DataFrame and Series objects. And seaborn further simplify the procedures. Unfortuantely, seaborn doesn’t have built-in support for 3D functionalities. However, we can still use seaborn style for 3D matplotlib plots. Let’s learn the basics of pandas and seaborn through some simple examples.
Flight Dataset
The dataset used will be the flight dataset, which has 10 years of monthly airline passenger data.
import seaborn as sn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sn.set(style='darkgrid')
data = pd.read_csv('flight.csv', sep=',')
data
Out[95]:
year month passengers
0 1949 January 112
1 1949 February 118
2 1949 March 132
3 1949 April 129
4 1949 May 121
.. ... ... ...
139 1960 August 606
140 1960 September 508
141 1960 October 461
142 1960 November 390
143 1960 December 432
[144 rows x 3 columns]
# check the detailed info of the dataset
data.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 144 entries, 0 to 143
Data columns (total 3 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 year 144 non-null int64
1 month 144 non-null object
2 passengers 144 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(2), object(1)
memory usage: 3.5+ KB
pandas.DataFrame.plot()
In pandas, the plot method on Series and DataFrame is just a simple wrapper around plt.plot(), with some additional parameters.
DataFrame.plot(*args, **kwargs)
Here is a list of the parameters, where the kind can be used to indicate the type of the plot:
xykindline: line plot (default)bar: vertical bar plotbarh: horizontal bar plothist: histogrambox: boxplotkde: Kernel Density Estimation plotdensity: same askdearea: area plotpie: pie plotscatter: scatter plot (DataFrame only)hexbin: hexbin plot (DataFrame only)
axsubplotsharexshareylayoutfigsizeuse_inextitlegridlegendstylelogxlogyloglogxticksyticksxlimylimxlabelylabelrotfontsizecolormapcolorbarpositiontableyerrxerrstackedsort_columnssecondary_ymark_rightinclude_bool- `backed’
Now, let’s consider plotting a line graph of columns ‘year’ and ‘passengers’ using DataFrame.plot(), which will create something like this:
plt.figure()
data.plot(x = 'year', y = 'passengers')
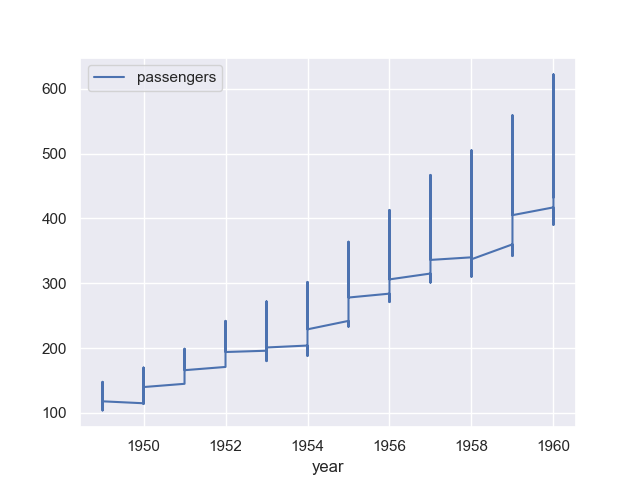
The graph looks kind of weired. We will improve it using seaborn below. Let’s now draw the line graph in groups grouped by month.
Firstly, we need to convert it to a pivot table:
data_wide = data.pivot("year", "month", "passengers")
data_wide
Out[102]:
month April August December February ... May November October September
year ...
1949 129 148 118 118 ... 121 104 119 136
1950 135 170 140 126 ... 125 114 133 158
1951 163 199 166 150 ... 172 146 162 184
1952 181 242 194 180 ... 183 172 191 209
1953 235 272 201 196 ... 229 180 211 237
1954 227 293 229 188 ... 234 203 229 259
1955 269 347 278 233 ... 270 237 274 312
1956 313 405 306 277 ... 318 271 306 355
1957 348 467 336 301 ... 355 305 347 404
1958 348 505 337 318 ... 363 310 359 404
1959 396 559 405 342 ... 420 362 407 463
1960 461 606 432 391 ... 472 390 461 508
[12 rows x 12 columns]
Now we can plot the graph simply by data_wide.plot(), which creates the graph below.
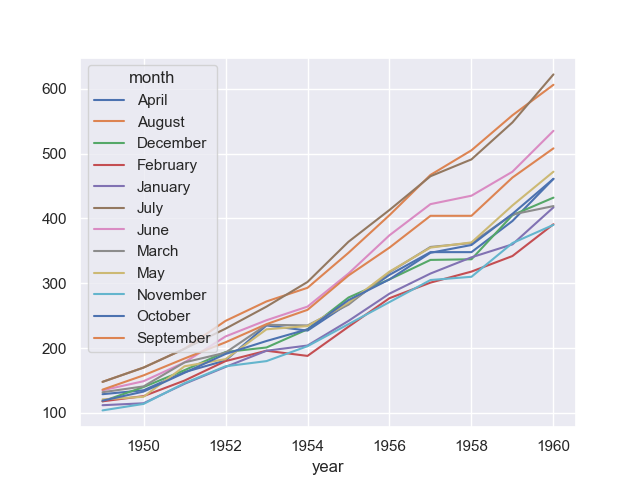
seaborn.lineplot()
Let’s consider improving the line graph using seaborn.lineplot().
By default, seaborn.lineplot() will plot mean and 95% confidence levels, making it look much better:
plt.figure()
sn.lineplot(x = 'year', y = 'passengers', data=data)
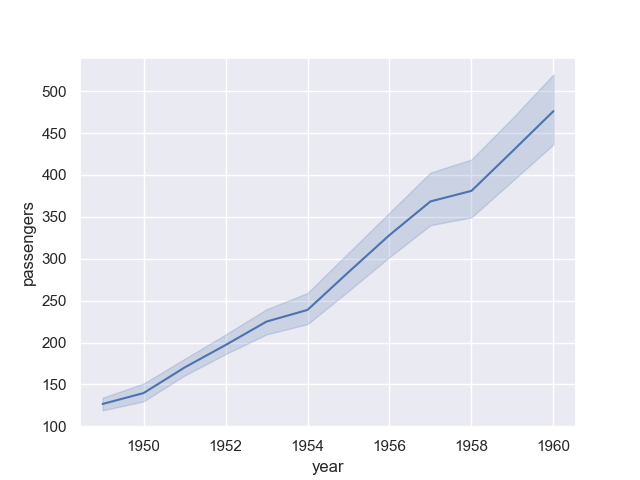
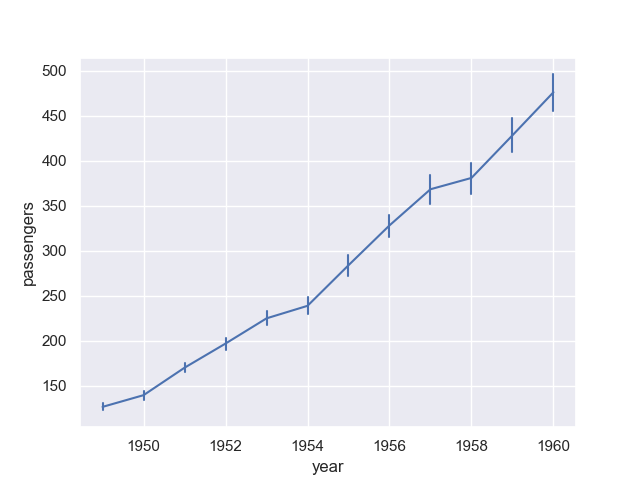
The confidence interval is displayed in translucent error bands by default and with 95% confidence level. We can also change the error style to ‘bars’ by parameter err_style and confidence level by parameter ci:
plt.figure()
sn.lineplot(x = 'year', y = 'passengers', data = data,
err_style = 'bars', ci = 95)
To group the data, we can use parameter hue, size or style (which is very convenient):
plt.figure()
sn.lineplot(x = 'year', y = 'passengers', hue = 'month', data = data)
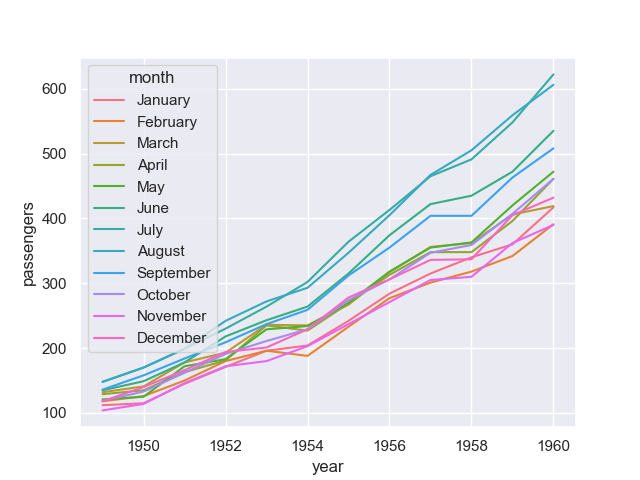
To distinguish the groups, besides different line styles, we can also use markers for different groups using markers:
plt.figure()
sn.lineplot(x = 'year', y = 'passengers', hue = 'month', data = data,
style = 'month', markers=True)
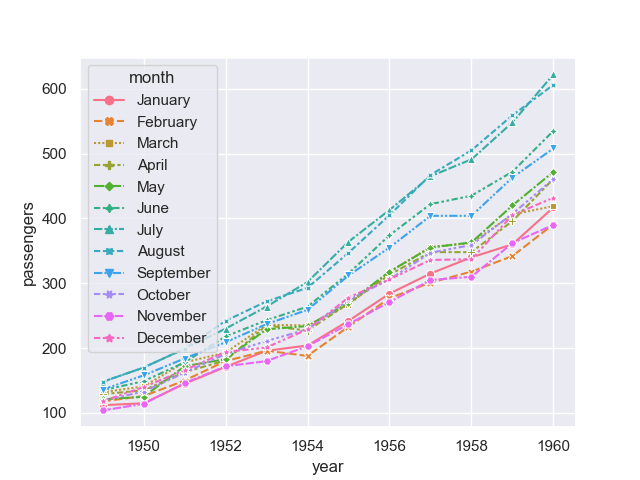
Now, the line graph looks much better.
Reference to DataFrame.plot() and seaborn.lineplot()
Others Plots: Overview
pandas
- In addition to the
kindparameter inDataFrame.plot(), there are theDataFrame.hist()andDataFrame.boxplot()methods, which use a separate interface. - We can also use the methods
DataFrame.plot.<kind>, including:DataFrame.plot.areaDataFrame.plot.barhDataFrame.plot.densityDataFrame.plot.histDataFrame.plot.lineDataFrame.plot.scatterDataFrame.plot.barDataFrame.plot.boxDataFrame.plot.hexbinDataFrame.plot.kdeDataFrame.plot.pie
- There are also several plotting functions in
pandas.plottingthat take a Series or DataFrame as an argument, including:andrews_curvesautocorrelation_plotbootstrap_plotboxplotlag_plotparallel_coordinatesradvizscatter_matrix
seaborn
- Relational plots
replot: Figure-level interface for drawing relational plots onto a FacetGrid.scatterplotlineplot
- Distribution plots
displot: Figure-level interface for drawing distribution plots onto a FacetGrid.histplotkdeplot: Plot univariate or bivariate distributions using kernel density estimation.ecdfplot: Plot empirical cumulative distribution functions.rugplot: Plot marginal distributions by drawing ticks along the x and y axes.
- Categorical plots
catplot: Figure-level interface for drawing categorical plots onto a FacetGrid.stripplot: Draw a scatterplot where one variable is categorical.swarmplot: Draw a categorical scatterplot with non-overlapping points.boxplot: Draw a box plot to show distributions with respect to categories.violinplot: Draw a combination of boxplot and kernel density estimate.boxenplot: Draw an enhanced box plot for larger datasets.pointplot: Show point estimates and confidence intervals using scatter plot glyphs.barplot: Show point estimates and confidence intervals as rectangular bars.countplot: Show the counts of observations in each categorical bin using bars.
- Regression plots
lmplot: Plot data and regression model fits across a FacetGrid.regplotresidplot
- Matrix plots
heatmapclustermap
- Multiplot grids
FacetGrid: Multi-plot grid for plotting conditional relationships.pairplot: Plot pairwise relationships in a dataset.PairGrid: Subplot grid for plotting pairwise relationships in a dataset.joinplot: Draw a plot of two variables with bivariate and univariate graphs.JointGrid: Grid for drawing a bivariate plot with marginal univariate plots.
An overview of seaborn can be referenced to this page. We will delve deeper into these plots in the future plots.

Comments